Pneumonia, a respiratory condition characterized by inflammation in the lungs, can also affect our feline friends. Cats can develop pneumonia due to various causes, including bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, as well as aspiration of foreign objects or irritating substances. Understanding the risk factors and recognizing the signs and symptoms of pneumonia in cats is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, prevention, management, and long-term effects of pneumonia in cats.
Causes and risk factors of pneumonia in cats
Pneumonia in cats can be caused by a range of factors, including bacterial infections such as Bordetella bronchiseptica, viral infections such as feline herpesvirus, or fungal infections such as Aspergillus. Cats with compromised immune systems, such as those with feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) or feline leukemia virus (FeLV), are more susceptible to developing pneumonia. Additionally, cats living in crowded or stressful environments, or those exposed to secondhand smoke, are also at a higher risk.
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia in cats
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of pneumonia in cats is essential for early intervention. Common symptoms include coughing, rapid breathing, difficulty breathing, wheezing, sneezing, nasal discharge, lethargy, loss of appetite, and weight loss. Cats with pneumonia may also have a fever and exhibit open-mouth breathing or stretch their necks out to breathe. If you notice any of these signs, it is crucial to seek veterinary care promptly.
Diagnosing pneumonia in cats
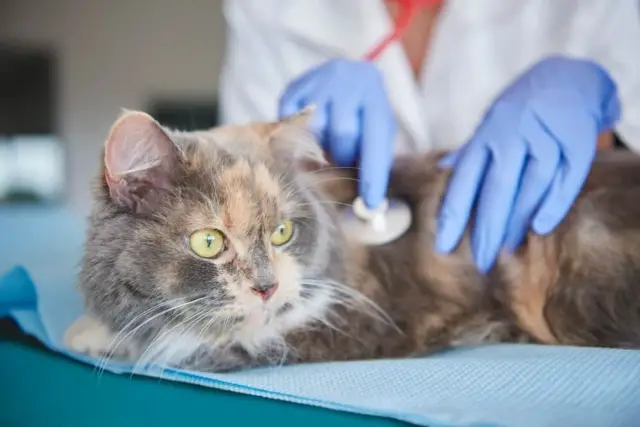
To diagnose pneumonia in cats, veterinarians may perform a combination of physical examination, blood tests, chest X-rays, and bacterial or fungal cultures. During the physical examination, the veterinarian will listen to the cat’s lungs using a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds or crackles. Blood tests can help assess the cat’s overall health and detect any underlying infections. Chest X-rays provide a detailed image of the lungs, revealing any abnormalities or signs of inflammation. Bacterial or fungal cultures may be conducted to identify the specific pathogen causing the pneumonia.
Treating pneumonia in cats
The treatment approach for pneumonia in cats depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In bacterial pneumonia cases, antibiotics are typically prescribed to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. Antiviral medications may be administered for viral pneumonia, while antifungal drugs are used to treat fungal pneumonia. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids. It is crucial to follow the veterinarian’s instructions carefully and complete the entire course of medication to ensure effective treatment.
Preventing pneumonia in cats
Prevention plays a vital role in minimizing the risk of pneumonia in cats. Vaccination against common respiratory pathogens, such as feline herpesvirus and feline calicivirus, can help protect cats from developing pneumonia. Maintaining a clean and stress-free environment, avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke, and keeping cats away from potentially hazardous substances can also reduce the risk of pneumonia. Regular veterinary check-ups and prompt treatment of any underlying health conditions can further contribute to preventing pneumonia in cats.
Managing pneumonia in cats at home
Once diagnosed with pneumonia, cats may require additional care at home to aid recovery. Providing a warm and quiet environment can help reduce stress and facilitate healing. Ensure that your cat has access to fresh water and a balanced diet to support their immune system. Administer any prescribed medications as directed by the veterinarian, and monitor your cat’s symptoms closely. If your cat’s condition worsens or if you notice any new or concerning symptoms, contact your veterinarian immediately.
When to seek veterinary care for pneumonia in cats
It is crucial to seek veterinary care as soon as you suspect your cat may have pneumonia. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of a successful recovery. If your cat exhibits any signs of respiratory distress, such as open-mouth breathing, bluish gums, or extreme lethargy, it is considered an emergency, and immediate veterinary attention is required. Do not hesitate to contact your veterinarian if you have any concerns or questions regarding your cat’s health.
Complications and long-term effects of pneumonia in cats
While most cases of pneumonia in cats can be successfully treated, complications and long-term effects can occur, especially in severe or untreated cases. Pneumonia can lead to secondary infections, such as bronchitis or pleuritis, which may require additional treatment. In some instances, pneumonia can cause scarring in the lungs, leading to chronic respiratory issues. Regular follow-up appointments with your veterinarian are essential to monitor your cat’s lung health and address any potential complications.
Conclusion and resources for further information
Preventing and managing pneumonia in cats requires a proactive approach to their health and well-being. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking prompt veterinary care, we can ensure the best possible outcome for our feline companions. Remember to follow your veterinarian’s advice, maintain a clean and stress-free environment, and prioritize preventive measures such as vaccinations. If you have any questions or concerns about pneumonia in cats, consult your veterinarian for personalized guidance. Your cat’s respiratory health is of utmost importance, and with proper care, we can help them lead happy and healthy lives.
If you enjoyed my article, I would appreciate you sharing it with your network.

Sima Ndlebe
Sima writes for CatBuzz. He is interested in Cats, Health and Fitness, and Entrepreneurship.
Published: 11 October 2023
Related Articles
Disclaimer
The content found on CatBuzz.org is presented on an "as is" basis and is intended for general consumer information and education purposes only. Any utilization of this information is voluntary and solely at the user's own risk.
None of the articles or content should be regarded as, or used in place of, veterinary medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The information provided on the website is purely for educational and informational intentions and should not be considered a substitute for professional guidance from a veterinarian or other qualified expert. The articles are designed to inform consumers about veterinary healthcare and medical matters that may impact their cat's daily life. It should be noted that this website and its services do not constitute the practice of any form of veterinary medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. CatBuzz.org explicitly disclaims any liability for any direct or indirect damages or losses that may arise from the use of or reliance on the information contained within the content.
Consumers must consult a veterinarian, veterinary specialist, or another qualified veterinary healthcare provider when seeking advice regarding their cat's health or medical conditions. It is important not to ignore, avoid, or postpone seeking medical advice from a veterinarian or other qualified veterinary healthcare provider solely based on information obtained from this website. If you believe that your cat may be experiencing a medical issue or condition, it is imperative to promptly contact a qualified veterinary healthcare professional.



